Types of Ischaemic Stroke
In this type of stroke the clot forms locally in one of the small blood vessels of the brain. Patient with Diabetes, high blood pressure and who smoke are at particular risk of getting this kind of disease
In this type of stroke a clot forms in one of the larger blood vessels of the neck or brain proximally and then breaks off and goes further into a smaller vessel distally to block it off completely. Patients with high blood pressure, diabetes, high cholesterol and smoking are at particular risk. The cause of this kind of stroke should be routinely screened for with some form of blood vessel imaging modality.
In this kind of stroke a clot forms in the heart and then flows into the brain to cause a stroke. AF is the largest killer in this type of stroke, but certain other heart valve diseases and heart failure also confers some risk. The cause of this kind of stroke should be routinely screened for with Echocardiogram, ECG and often prolonged monitoring of heart rhythms.
Certain infections of the brain can affect the blood vessels and cause stroke. In Indian population the commonest of such infections is tuberculosis. The next commonest are viral infections of brain including HIV (AIDS).
Inflammation of brain blood vessels can cause small strokes in different areas of the brain. While infections as detailed above can cause inflammation of brain blood vessels, the process can happen on its own without any reason. This is called Central nervous system vasculitis, or Primary Angitis of the Central nervous system
There are certain genetic diseases which can affect small blood vessels of the brain and mostly cause recurrent small strokes in deep areas of the brain. Generally this is associated with cognitive impairment of brain and confusion lasting over months. They include certain diseases of inability to process glucose (Glycogen storage diseases) which can cause stroke in infants and young adults. While others like CADASIL and MELAS cause strokes later in life between 40 to 55 years of life
Risk Factors
Age
GenderMales are more likely to suffer from stoke than females
Smoking
Diabetes Mellitus Obesity Hypertension (High blood pressure) High cholesterol Heart disease (Angina, heart attack, heart valve problems) Atrial Fibrillation (Irregular heart rhythm)A special mention has to be made here about Atrial Fibrillation or AF as it is known in the short form. In western and Caucasian population this is estimated to be prevalent in approximately 25% of population and is widely regarded as the most important risk factor for Ischaemic stroke. In some patients this may confer a stroke risk in excess of 20% per year. In UK doctors are expected to screen for AF routinely even if they come for some other reason to increase capture of this disease and institute stroke prevention measures early. It is not known as to what extent this disease affects Indian population, but there is no reason why it should be a lesser problem in India. Screening programmes need to be developed to actively look for this disease.
Symptoms of Ischaemic Stroke
Recognising stroke early is of paramount importance as there is only a short time window where the treatment is effective and brain damage can be reversed. To provide advanced medical interventions in a timely manner a stroke needs to be recognised early across the board, by patients, their family members and medical professionals
The person who is having the stroke may not recognise what is happening to him as his brain is not working. Therefore it is useful for all to have an awareness of symptoms of stroke so that people around the victim can recognise the problem and ask for help early. This necessitates development of simple and easy to use assessment tools to be used by Non Stroke specialist doctors, Allied health professionals and bystanders to recognise Stroke. Awareness programmes play a vital role to make the general population aware of the importance of recognising stroke early and how to use the assessment tools to do so
A few assessment tools which are in common practice in the developed countries has been decribed below
 The FAST tool has been developed and is commonly used in the United Kingdom. It is an assessment tool for use of lay persons and bystanders to quickly recognise Stroke and urgently seek medical help. Significant efforts have been made in recent years to spread the awareness about this tool among general population including widespread campaign through public media. The tool involves quick assessment of facial asymmetry, power of arms and speech of patient within the ability of a layperson as described below.
The FAST tool has been developed and is commonly used in the United Kingdom. It is an assessment tool for use of lay persons and bystanders to quickly recognise Stroke and urgently seek medical help. Significant efforts have been made in recent years to spread the awareness about this tool among general population including widespread campaign through public media. The tool involves quick assessment of facial asymmetry, power of arms and speech of patient within the ability of a layperson as described below.
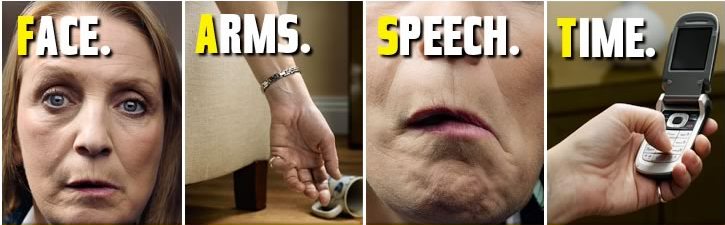
Ask patient to show teeth, Is there an unequal smile or grimace
Note which side does not move wellLift the patient’s arms together to 90º if sitting, 45º if supine and ask them to hold the position for 5 seconds before letting go, does one arm drift down or fall rapidly?
If one arm drifts down or falls, note whether it is the patient’s left or right.Listen for NEW disturbance of speech, or slurred speech.Listen for word-finding difficulties with hesitations.
Asking the patient to name common objects like a cup, key or watch.IS THIS NORMAL FOR THEMIt's TIME to ring an emergency ambulance
The FAST tool have become very popular in recent years and work as an effective means of recognising stroke early and getting immediate medical attention Click here to watch a relevant video(THE FAST TEST)
ROSIER: The Rosier tool which stands short for Recognition of Stroke in Emergency Room was developed to help early recognition of stroke in the Emergency Department by Non Stroke specialist doctors. There are of course a number of conditions which may mimic stroke at the onset and make diagnosis difficult for non specialists. The ROSIER is specifically aimed to help to differentiate these Stroke mimics from an Acute Stroke.
Click here to download a sample Rosier Scoring System document
Investigation of Ischaemic Stroke
Brain scan: Doctors usually ask for a CT scan of brain. On special circumstances when there is confusion over diagnosis a MRI scan can be advised.
Vascular (blood vessel) imaging: This is done to image the blood vessels of neck and brain to identify any clots or cholesterol deposits. The various modalities available are Doppler, CT Angiogram and MR Angiogram.
Blood tests: These should include routine blood tests and specific ones to screen for diabetes and high cholesterol.
ECG: This is a heart tracing and will identify heart problems including Atrial fibrillation.
Echocardiogram: This is a heart scan that can identify any problem with the structure of the heart including any defects of heart valves.
Prolonged cardiac monitoring:This is an important modality to pick up Atrial fibrillation which is otherwise not diagnosed. It is very important to screen for this disease as it is widely regarded as the most important risk factor for stroke. The irregularity of heart rhythm could be periodic with the heart remaining in normal rhythm for rest of the time. A single examination or ECG therefore may not be able to pick up AF. It is therefore necessary to monitor cardiac rhythm for a stipulated time period to detect AF. Evidence suggests that the pick up of AF is maximised after stroke if monitored for 3-7 days.
Emergency treatment of Ischaemic stroke
We now know that parts of the brain affected by stroke does not immediately die once the blood supply to its part is cut off. It regulates its own blood supply, opens up new blood vessels and tries to keep the affected part alive (albeit in a state of shock) for some time. Evidence suggests that it is able to do so up to a time period of 4.5 – 6 hours. If the clot can be broken off and blood supply restored to brain within this time period then there is a good chance of recovery and limiting brain damage.
Following forms of treatment are proven to be effective and is routine practice in the Western countries.
Specialised stroke unit care: There is now clear evidence that stroke patients who are cared for in specialised stroke units geared up to cater to their specific needs and able to provide specialised care as detailed below does much better than patients cared in routine wards. There is clear evidence that it reduces death and disability. Once recognised to be having a stroke the patient should be rushed to a hospital or institute which has a specialised stroke unit and offers specialist stroke care.
Intravenous Thrombolysis:
This concept involves giving a clot bursting drug to break the clot in the blood vessel and restore blood supply back to the brain. The drug commonly used in called Alteplase. A part of it is given quickly in the blood stream and the rest is given slowly over an hour. There is evidence that if this can be done within 4.5 hours from stroke onset then it is effective and can potentially limit brain damage and disability. The most recent medical trials have suggested that this may be effective up to 6 hours from stroke onset but this is not entirely clear as yet.
One in three patients who have been given this drug within 4.5 hours stands a chance of good recovery. The chances are even better if this can be given within 3 hours. The most important complication of this drug is bleeding in the brain. While most bleedings are small, harmless and cause no major problem, about 1-2% of patients receiving this drug will develop serious bleeding complications which can be life threatening. Patients and families who receive this drug should be given this information and appropriately consented. Reassuringly despite the complication the drug does not cause any increase in number of deaths in stroke patients. It is the approved treatment for strokes in Europe, UK and North America and deemed to be safe.
Intra arterial Thrombectomy This procedure is similar to angioplastyperformed for heart attack by cardiologists. It is performed byInterventional Neuroradiologist. Initially an angiogram identifies where the clot is located in the brain.The radiologist then introduces a guidewire into the blood vessel from wrist or groin and guides it up to the clot in the brain. Various devices and techniques are then employed to break the clot open and restore the blood supply back to brain. Current evidence suggests that this technique should be used in conjunction with Intravenous Thrombolysis described above. However the bleeding rates in this procedure is thought to be lesser.
Antiplatelet therapy: Aspirin at a high dose of 300 mg per day can be used as an effective treatment after stroke. The risk of stroke recurrence after a patient has suffered a stroke is very high. Aspirin effectively reduces this recurrence risk. However it has no effect on the stroke or brain damage that has already happened.
Swallowing assessment: In stroke patients the muscles of swallowing,breathing and coughing could be paralysed. Often food, drink or their own saliva can go down the wrong way to their lungs to cause infection and pneumonia. An urgent swallowing assessment should be performed in all stroke patients to demonstrate that they can safely swallow food and drink and reduce the chances of pneumonia. If not then an alternate feeding method (via tubes through nose or directly in the stomach) must be established.
Blood pressure management: If the patient has experienced Intravenous thrombolysis and/or intra arterial thrombectomy blood pressure needs to be monitored intensively, preferably in a neuro intensive care unit for 4 hours. Various medicines can be used through a drip to keep the blood pressure in desired level. If the patient has not been given thrombolysis/thrombectomy treatment then it is appropriate to allow the brain to autoregulate the blood pressure and not intervene with it for 7-10 days. It is often expected that the blood pressure will remain on the higher side during this period. This is not harmful to the brain or body.
Blood glucose monitoring: It is believed that strict control of blood glucose after the immediate aftermath of stroke is beneficial to limit brain damage. This is done by infusing a drip of insulin through the veins with hourly checks on blood glucose.
Early mobilisation: Immobilisation in bed after a stroke causes many complications. This includes pneumonia, muscle disuse and weakness and new clots in leg and lung. Early mobilisation out of bed and sitting out in chair has to be attempted to reduce these complications and bring a favourable outcome to subsequent rehabilitation
Decompressive hemicraniectomy:On occasions after a large stroke the brain tissue can swell and cause pressure on the brain which can lead to life threatening situation. An operation called Decompressive hemicraniectomy which takes a bit of bone away from the skull to help relieve this pressure can be life saving. Approximately 50% of patients having this operation will survive. It is generally believed to be successful in patients less than 60 years of age with good health before the stroke and when done within 48 hours of stroke onset. However carefully selected patients may benefit from this operation up to 96 hours from the start of the stroke.
Longterm Treatment of Ischaemic stroke
Antiplatelet therapy Antiplatelet group of drugs thin the blood and prevent further clot formation. Recurrence rates of stroke and heart attack amongst stroke victims is very high, especially within the 1st year. An antiplatelet should be continued therefore to prevent clot formation and recurrence for lifetime after stroke. The recommended drug for this is Clopidogrel. Combination of aspirin and Clopidogrel which is commonly used after heart attack should not be used after stroke and may be harmful causing excessive bleeding.
Anticoagulation: If the stroke is suspected to have come from cardiac embolism (clot thrown off the heart) i.e. originated from the heart due to Atrial Fibrillation or other valve diseases then Clopidogrel is not strong enough to prevent recurrence. Use of stronger medicines is recommended to thin the blood more to prevent clot formation. Recommended drugs for this purpose are warfarin, sinthrome and a group of newer Novel Anticoagulating agents (NOAC – dabigatran, rivoroxaban, apixaban, edoxaban). Warfarin and Sinthrome needs to be monitored carefully with regular blood tests. Important complication for all drugs in this group is predisposition to bleeding. The NOAC group does not need regular blood tests for monitoring and is likely to cause less complications with bleeding inside the brain; however this group is still not widely available in India.
Diabetes Mellitus All patients should be screened for this and managed with medicines if diagnosed.
Cholesterol: All patients should be screened for high cholesterol and started on a cholesterol lowering medication if found to be high. The commonest group of drugs used for this purpose is “Statins”.
Blood pressure: All patients should be screened for high blood pressure. This should be lowered and managed aggressively after 7-10 days after Ischaemic stroke.
Smoking cessation: All smokers should be given counselling and help to stop smoking.
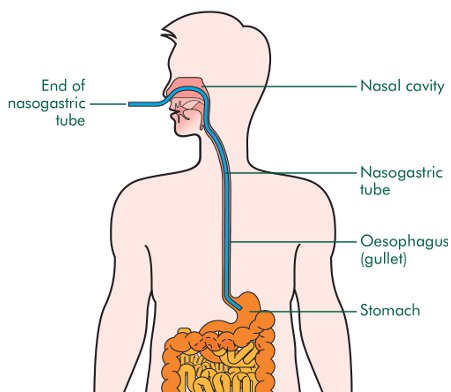
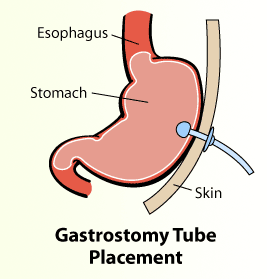
Feeding: All stroke patients should receive dietician input to establish a feeding regime. Nutrition after stroke is extremely important to maintain muscle bulk and power and therefore has a positive influence on rehabilitation outcome. If the swallowing assessment shows that the patient is not able to swallow safely then alternate methods of feeding should be implemented urgently. A nasogastric tube should be used in the immediate period after stroke. This is a tube passed through nose into the stomach through which food can be passed without the patient swallowing. If after 4 weeks the swallowing is still deemed to be unsafe a PEG (gastrostomy) tube should be considered. This involves passing a tube directly into the stomach of the patient through a hole on the skin above the stomach. This can be used as a more permanent method of feeding the patient.
Video credit attributed to: http://pocketsnips.org
Picture credit attributed to: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nasogastric_intubation
Picture credit attributed to :http://www.oralcancerfoundation.org/
Carotid surgery: Vascular imaging is routinely done after stroke to identify any clots or cholesterol plaques in carotid blood vessels (major blood vessels in neck that supply the brain). If the blood vessel is found to be > 70% narrow a carotid surgery is often recommended. A surgery called Carotid Endarterectomy (CEA) is generally preferred, but for patients who are unable to undergo surgery a carotid stenting can also be offered. CEA can be considered in male patients under 75 years of age if the artery is 50 – 70% narrow as well. For minor strokes the surgery should be done within 2 weeks. For larger strokes this should be delayed until the patient is stable but should be performed within 3 months. Surgery beyond 3 months confers much less benefit and is questionable. While this is performed in North America under patient choice, UK takes a more conservative approach and manages this with medicines.
Rehabilitation: The scope of this topic is large and we are only going to touch on this currently. The natural history o Ischaemic stroke will suggest that the disability will be most at onset and then improve from thereon. The most improvement is in the 1st two weeks, followed by continuous improvement for next 3 months. Most patients will plateau after this, but some continue to improve up to a year after stroke. Early mobilisation and rehabilitation is paramount to reduce disability after stroke. This is a multidisciplinary approach involving physiotherapists, occupational therapists, speech therapists, swallowing specialists and of course the stroke doctor. Various exercises are directed at improving muscle power and balance by physiotherapists while occupational therapists work with more complex tasks like dressing one self. Mental exercises are also used to improve brain functioning in various fields. Loss of speech is a common symptom after stroke and the speech therapists teach various techniques for the brain to overcome or work round these problems. It is recommended that able patients receive 45 minutes of rehabilitation from each of these specialists every day.
In essence, parts of the body have to re-learn the vary basic activities like moving, swallowing, speaking etc following a stroke and it is only achievable with help from well trained and specialist team of physiotherapists, occupational therapists and speech therapists.
Complications after Ischaemic stroke
Post stroke pneumonia:
Pneumonia or severe chest infection is one of the commonest complications after stroke. Often after stroke the muscles inside the mouth used for swallowing are paralysed, as well as the muscles used for coughing. This results in food, drinks and patients own saliva going down the air pipe into the lungs causing pneumonia. Between 20 – 30% of patients with stroke will develop a chest infection of some sort. This is a dreaded complication which increases the chances of death significantly post stroke. Patients with large strokes who have lost swallowing function are at particular risk. Immediate assessment of swallowing function post stroke is the most important step to prevent post stroke pneumonia. If the test suggests problem with swallowing then the patient should not be allowed to eat or drink normally, but should be fed through a tube inserted through nose or mouth.
Post stroke pneumonia is diagnosed with help of clinical examination, chest x-ray, blood tests. It should be treated aggressively with antibiotics through the drip into the veins.
Malignant Stroke: On occasions after a large stroke the brain tissue can swell and cause pressure on the brain which can lead to life threatening situation. An operation called Decompressive hemicraniectomy which takes a bit of bone away from the skull to help relieve this pressure can be life saving. Approximately 50% of patients having this operation will survive. It is generally believed to be successful in patients less than 60 years of age with good health before the stroke and when done within 48 hours of stroke onset. However carefully selected patients may benefit from this operation up to 96 hours from the start of the stroke.
Clotting in Leg (Deep vein thrombosis): In a normal scenario when a person walks or moves the muscles of leg and calf contracts and this helps to get the blood flow back to the heart. Often patients after stroke, especially ones who have suffered a large stroke, are kept immobile in bed. This results in blood pooling and being stagnant in their legs with compromised blood flow. As a result often blood clots in their leg causing deep vein thrombosis (DVT). The symptoms are swelling, redness and pain in leg. Early mobilisation after a stroke is paramount in preventing clot formation in leg. Recently use of electronic devices (IPC or Flotron boots) which makes the calf muscles contract periodically when the patient is at rest has been shown to reduce these complications. It is treated with medication like warfarin or heparin (anticoagulation) to thin the blood and not allow it to clot further. The duration of treatment is usually between 3 to 6 months.
Clotting in Lung (Pulmonary embolism): The mechanism of developing this complication post stroke is similar to formation of clots in leg. Due to relative immobilisation of the patient post stroke, clots form in leg and can then migrate with blood flow directly to lung. Clot in lung (Pulmonary embolism) though is a much more serious and life threatening complication than clot in leg (DVT). Measures to prevent are similar to above in early and active mobilisation post stroke, use of electronic devices (IPC or Flotron boots). If confirmed this should be treated immediately with medication that prevents further clot formation like warfarin or heparin (anticoagulation). In special circumstances a device like an umbrella is placed in the blood vessel between the leg and lung to prevent migration of clots from leg to lung. The device is placed in a blood vessel called Inferior vena cava (IVC) and is therefore called IVC filter. It is placed under radiological guidance through a small cut in the groin. It is usually a straightforward procedure with very few complications. The device may be taken out later if needed.
Post stroke seizures:
Seizures or fits (similar to attacks in patients with epilepsy) are an extremely common complication after stroke. It is relatively uncommon to occur at the onset for Ischaemic stroke, but may occur anytime afterwards from the first week to 20 years afterwards. Common symptoms may range from violent shaking of all arms and legs, to twitching or rhythmical shaking of a particular arm or leg or simply vacant looks and being unresponsive for some time. Patients may be drowsy or irritable after an event and often complain of a headache.
It is generally diagnosed from accounts of events given by patient’s relatives or other witnesses to the events. An EEG (study of electric waves in brain; generally done by putting electrodes on the head and studying the electric impulses) is often done but gives limited information towards a diagnosis. It is treated with antiepileptic medications which prevent seizures. Common medications used are Sodium Valproate, Levetiracetam (Keppra) and lamotrigine.
Post stroke spasticity (muscle stiffness): After stroke often muscles develop severe stiffness due to long term remaining paralysed and unused. Usual symptoms are pain in muscles and difficulty and resistance in moving joints. This can be treated with muscle relaxant medication initially. On occasions this is treated with an injection of muscle relaxant (Botulinum toxin, BOTOX) directly into the muscle.
